How to 3D Scan an Object with a Portable Structured-Light Scanner
02/22/25
In the world of 3D technology, understanding how to effectively utilize a professional 3D scanner can significantly enhance the quality and efficiency of your projects. A high precision 3D scanner, like a portable structured-light scanner, offers remarkable capabilities for capturing intricate details of objects. In this guide, we will explore the process of 3D scanning an object using this innovative technology, with insights from 3DeVOK, a leader in advanced 3D scanning solutions.
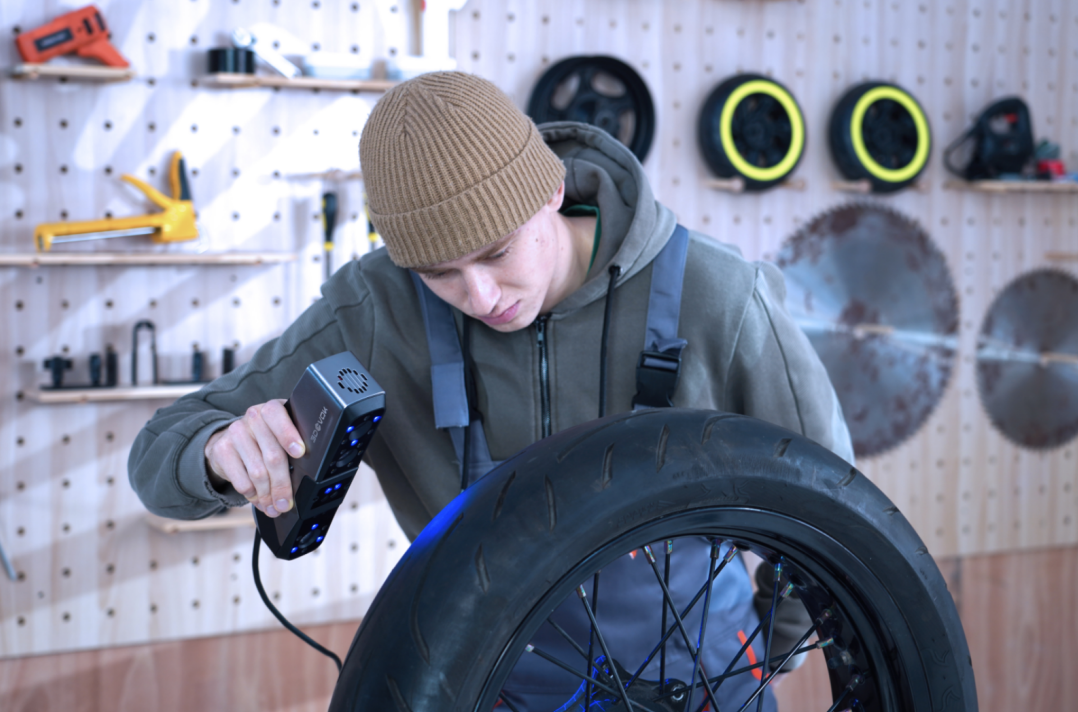

A professional 3D scanner using structured light works by projecting a series of light patterns onto an object. The scanner captures the deformation of these patterns to create a 3D model. This method is particularly effective for capturing complex shapes and fine details, making it an excellent choice for various applications, including product design, art preservation, and medical imaging.
The structured-light technology allows for quick data acquisition, making it suitable for scanning objects of different sizes and materials. The portability of these scanners ensures that you can easily transport them to various locations, enhancing their versatility in the field.
Preparing for the 3D Scanning Process
Before you begin scanning, it’s essential to prepare both the object and the scanning environment:
- Choose the Right Object: Select an object that you wish to scan. Ensure it has sufficient surface details for the scanner to capture. Avoid overly shiny or transparent objects, as these can complicate data acquisition.
- Set Up the Environment: Ensure that the scanning area is well-lit but not overly bright, as direct light can interfere with the scanner’s performance. A controlled environment helps achieve optimal results.
- Stabilize the Object: If possible, secure the object in place to prevent movement during the scanning process. This stability is crucial for ensuring that the high precision 3D scanner captures accurate data.
Steps to 3D Scan an Object
Now that you’ve prepared the object and the environment, follow these steps to carry out the scanning process:
- Power On the Scanner: Turn on your professional 3D scanner and connect it to your computer or mobile device if required. Ensure that all necessary software is installed and updated.
- Calibrate the Scanner: Perform a calibration routine as specified by the manufacturer. This step is vital for ensuring accurate measurements and high-quality results.
- Position the Scanner: Place the high precision 3D scannerat an appropriate distance from the object. The optimal distance may vary based on the scanner’s specifications. Generally, you want to ensure that the entire object fits within the scanning field.
- Begin Scanning: Start the scanning process using the software provided with your scanner. The scanner will project light patterns onto the object and capture the resulting data. Move the scanner around the object to capture all angles and details, or rotate the object if it’s stationary.
- Monitor the Scan: Keep an eye on the scanning process via the software interface. Ensure that the coverage is complete and that there are no gaps in the data.
- Post-Processing: Once scanning is complete, use the software to process the captured data. This may involve cleaning up the model, filling in any holes, and refining the details to create a final 3D model.
Applications of Portable Structured-Light Scanners
A 3D scanner professional utilizes the power of structured light to serve various industries. For instance, in product design, accurate 3D models help engineers create prototypes and test designs effectively. In the healthcare sector, high precision 3D scanners are used for creating detailed anatomical models that aid in surgical planning.
Additionally, in the field of art and cultural heritage, portable structured-light scanners play a vital role in preserving artifacts by creating high-resolution digital replicas. The flexibility and portability of these scanners make them ideal for capturing data in various settings, whether in a studio or on-site.
Conclusion
Mastering the use of a high precision 3D scanner like a portable structured-light scanner can greatly enhance your capabilities in 3D modeling. By following the outlined steps, you can effectively scan objects and produce detailed digital representations. With the support of companies like 3DeVOK, you can access advanced technologies that facilitate innovation and efficiency in your workflows. As you explore the possibilities of 3D scanning, remember that the right tools and techniques can make all the difference in achieving your project goals.
Related Articles
View Our Product