Photogrammetry vs. 3D Scanning for Creating a 3D Model
03/04/25
In the realm of digital modeling, the methods of photogrammetry and 3D scanning are pivotal for creating accurate and detailed 3D scan models. Both techniques serve the essential purpose of translating physical objects into digital formats, but they employ different technologies and have unique advantages and applications. Understanding the distinctions between these approaches can help businesses choose the right method for their specific needs.
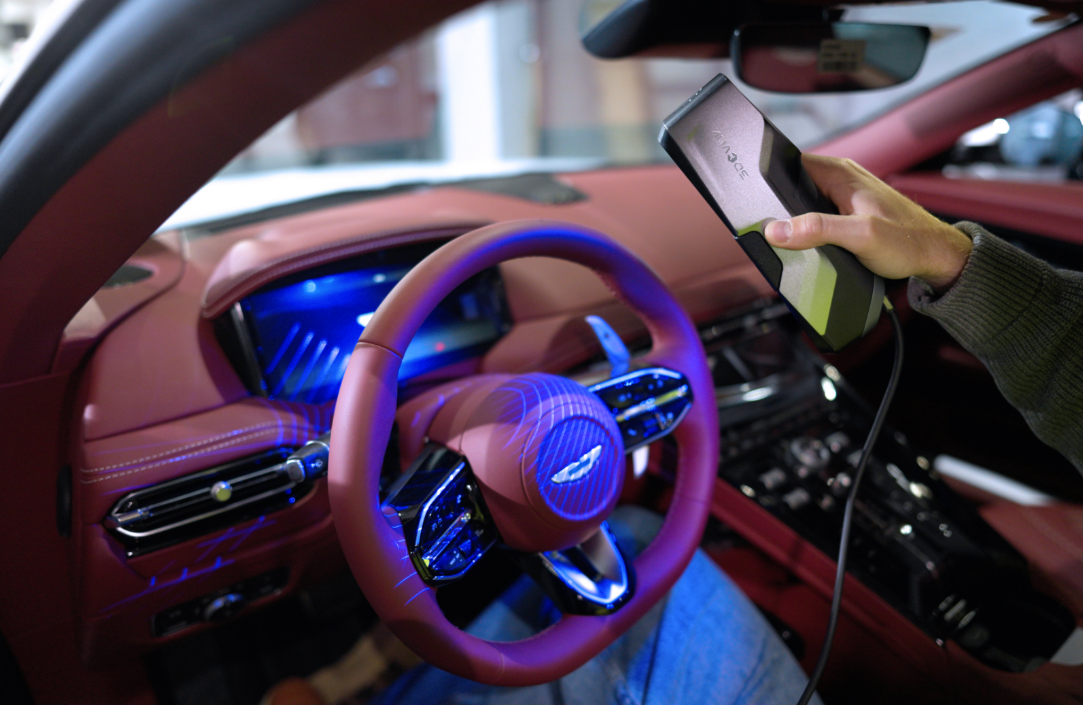

Scanned 3D models are crucial in various industries, including engineering, architecture, and healthcare. By utilizing advanced scanning technologies, companies can create precise digital copies of real-world objects, facilitating tasks such as reverse engineering, quality control, and product design. These models enhance collaboration among teams by allowing for effective visualization and manipulation of designs. With the ability to analyze and modify these 3D scan models, businesses can make informed decisions that improve efficiency and reduce costs.
The Role of Laser Scanning in Creating 3D Models
Laser scanning 3D models are known for their high degree of accuracy and detail, making them particularly effective for capturing complex geometries. For example, a laser scanner can deliver precise data that captures even the smallest details with exceptional clarity. This level of detail is invaluable in industries where precision is paramount, such as aerospace and automotive sectors. By integrating laser scanning technology, companies can ensure that their 3D scan models are reliable and accurate, leading to better decision-making and improved outcomes.
In contrast, photogrammetry utilizes photographs taken from different angles to reconstruct a 3D model. This method can be less accurate than laser scanning, especially for intricate details, but it excels in capturing color and texture. Photogrammetry is often more accessible, as it requires only a camera and applicable software, making it a popular choice for smaller projects or environments where budget constraints are a factor.
Comparing Photogrammetry and Laser Scanning
When considering 3D model reconstruction, both photogrammetry and laser scanning have their advantages. Laser scanning is typically favored for its precision and ability to capture complex shapes in detail, resulting in highly accurate scanned 3D models. This is especially important in fields such as heritage preservation, where exact replicas of structures are necessary for restoration.
On the other hand, photogrammetry is advantageous for its ability to cover larger areas and create visually rich models. It is particularly beneficial in fields like gaming and film, where the aesthetic quality of a model matters. The trade-off, however, is that photogrammetry may require extensive processing time to generate a usable model, whereas laser scanning often produces instant results.
For instance, using a laser scanning 3D model for a heritage site can yield precise measurements that help in restoration efforts, while photogrammetry can provide a vibrant digital representation that captures the essence of the site.
Applications of 3D Scan Models Across Industries
The applications of 3D scan models are diverse and expanding. In manufacturing, they are used for quality assurance, allowing companies to compare actual products against their digital representations to identify defects. In architecture, scanned 3D models are invaluable for documenting existing conditions, aiding renovations, and facilitating the design of new structures. Healthcare professionals utilize these models to create custom prosthetics and plan surgeries with greater precision.
Moreover, the integration of laser scanning 3D models into design workflows enhances efficiency by reducing the time spent on manual measurements and adjustments. As industries increasingly adopt digital tools, the demand for high-quality 3D scan models continues to rise. Companies must invest in reliable scanning technologies to remain competitive.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both photogrammetry and laser scanning are powerful methods for creating 3D model reconstruction. Each approach has its strengths and weaknesses, making them suitable for different applications. While laser scanning excels in accuracy and detail, photogrammetry offers a more accessible and visually rich alternative. At 3DeVOK, we recognize the importance of these technologies and their role in enhancing design and manufacturing processes. By leveraging the capabilities of both photogrammetry and laser scanning, businesses can create detailed and precise scanned 3D models, ensuring they are well-equipped to navigate the complexities of modern design and production. As the industry evolves, embracing these diverse tools will be crucial for maintaining a competitive edge.
Related Articles
View Our Product