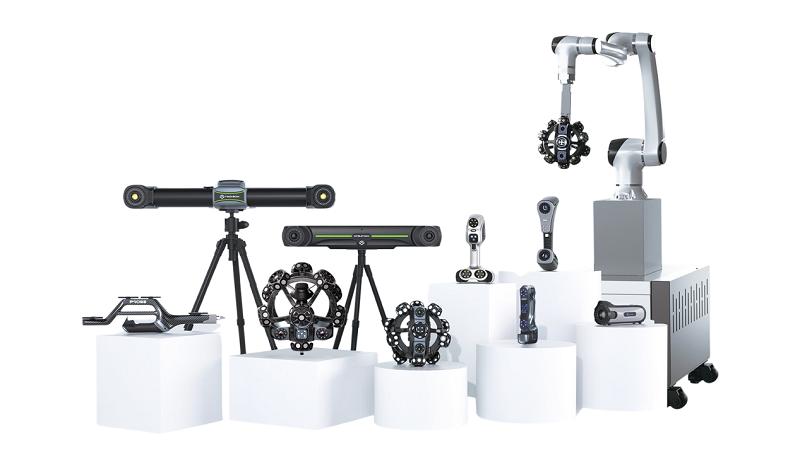
What is a 3D scanner?
11/13/24
With the rapid development of science and technology, the world we live in is becoming more and more digital. In this digital age, 3D technology is no longer out of reach. As the key equipment to realize this technology, 3D scanners are gradually coming into our view. So, what is a 3D scanner? How does it work?
I. The difference between 3D and 2D
First, we need to clarify the concept of “3D”. In mathematics and physics, “3D” is the abbreviation of Three-Dimension, that is, three-dimensional space, which includes three dimensions: x-axis (left and right), y-axis (front and back), and z-axis (vertical), forming the three-dimensional space we perceive. In contrast, 2D, that is, two-dimensional space, has only two dimensions, left and right and front and back, and no distinction between up and down, such as the common flat images we see.
II. Importance and functions of 3D scanning technology
Three-dimensional scanning, also known as 3D scanning, is a high-tech process that integrates optical, mechanical, electrical and computer technologies. It is mainly used to scan the spatial shape, structure and color of an object to obtain the spatial coordinates of the object surface. The significance of this technology lies in its ability to convert an object’s three-dimensional information into a digital format that can be directly processed by a computer, providing a very convenient and fast means for the digitization of the object. Three-dimensional scanning technology can achieve non-contact measurement, and has the advantages of fast speed and high precision. Its measurement results can be directly interfaced with a variety of software.
III. What is a 3D scanner?
As a vital component of modern digital technology, a handheld 3D scanner is a high-tech device that employs optical, laser, or other sensing technologies to capture geometric data from the surface of an object. Unlike traditional measuring tools, a professional 3D scanner can quickly and accurately capture the shape, size and appearance details of an object, and then generate a high-precision digital 3D model.
This device works like a digital copier, which can “copy” objects in the real world and convert them into a digital format that computers can understand and process. Many portable 3D scanners can not only capture the external form of an object, but also record the texture information of its surface.
IV. Working principle of 3D scanner
- Optical system: Laser 3D scanners scan objects through light sources such as laser, structured light or blue light, infrared light, etc. The light source shines on the object, and the reflected light generated is captured by the sensor.
- Data acquisition: The sensor (such as a camera or detector) records the position information of the reflected light, which contains the geometric data of the surface of the object.
- Data processing: Through software algorithms, the collected data is converted into a three-dimensional coordinate point cloud, and then a three-dimensional model of the object is constructed.
- Model reconstruction: The point cloud data is processed, including smoothing, denoising, and hole filling, and finally an accurate three-dimensional digital model is generated.
V. Application fields of 3D scanners
- Manufacturing and industry: reverse engineering, product testing, wing deformation monitoring, fuselage structure analysis, etc.;
- Education and research: scientific research education, experimental simulation, etc.;
- Virtual reality (VR/AR): 3D game modeling, 3D animation film production, 3D game stereo model input, etc.;
- Medical industry: 3D organ modeling, medical bionics, plastic surgery and orthodontic simulation and evaluation, etc.;
- Human body application: human body digitization, clothing CAD, human body modeling, human body digital sculpture, 3D facial recognition, etc.;
- Cultural and art: digital preservation and display of cultural relics, cultural relics restoration, digital museums, etc.;
- 3D printing: reverse 3D reconstruction, conversion of designed physical models into digital models, etc.
In short, 3D scanner is an advanced technology that can accurately digitize objects in the real world and convert them into 3D data that can be processed by computers. This technology not only promotes the progress of manufacturing, medical, education and other fields, but also provides us with more efficient and accurate customized services. With the continuous development of technology, the application prospects of color 3D scanners will be broader and will play a greater role in the future.
Related Articles
View Our Product